|
Size: 3812
Comment:
|
Size: 4181
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 48: | Line 48: |
| = Setup Virt Manager = | = Setup Virt Machine Manager = |
| Line 50: | Line 50: |
| == Start Virtual Machine Manager from Application Menu == | |
| Line 51: | Line 52: |
| {{attachment:00-Main-Start-Screen.png|Virtual Machine Manager|align="middle"}} | |
| Line 52: | Line 54: |
| === 01) Example OS Install Screen === | == 1) Click on "Create a new virtual machine" button for new VM creation == |
| Line 54: | Line 56: |
| {{attachment:01-Example-OS-Install-Screen.png|Debian Buster Install Screen|align="middle"}} | {{attachment:01-Create-New-VM.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 56: | Line 58: |
| === 02) Example Guest OS Grub2 Boot Screen === | === Choose install media (ISO image or CDROM) for installation from your downloaded favourite Linux Distro ISO image. === |
| Line 58: | Line 60: |
| {{attachment:02-Example-Guest-OS-Grub2-Boot-Screen.png|Installed Debian Buster Grub2 Boot Screen|align="middle"}} | == 2) Browse and choose the Linux Distro ISO image == |
| Line 60: | Line 62: |
| == Start Virt Manager from Application Menu == 00-Main-Start-Screen.png |
{{attachment:02-Choose-ISO-image.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 63: | Line 64: |
| 1) Click on "Create a new new virtual machine" button for new VM creation | == 3) Set Your required Memory and CPU settings for the VM (Guest OS) == {{attachment:03-Set-Memory-CPU.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 65: | Line 67: |
| 01-Create-New-VM.png | == 4) Enable and Create a storage space for the VM (Guest OS) == {{attachment:04-Create-Storage-Space.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 67: | Line 70: |
| Choose install media (ISO image or CDROM) for installation from your downloaded favourite Linux Distro ISO image. 2) Browse to and choose the Linux Distro ISO image 02-Choose-ISO-image.png 3) Set Your required Memory and CPU settings for the VM (Guest OS) 03-Set-Memory-CPU.png 4) Enable and Create a storage space for the VM (Guest OS) 04-Create-Storage-Space.png 5) Ready to begin the installation 05-Ready-VM-Install.png |
== 5) Ready to begin the installation == {{attachment:05-Ready-VM-Install.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 92: | Line 79: |
| 6) Example Linux Distro OS Install Start Screen | == 6) Example Linux Distro OS Install Start Screen == {{attachment:06-Example-Guest-OS-Install_Start.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 94: | Line 82: |
| 06-Example-Guest-OS-Install_Start.png | == 7) Example Installed Guest OS Boot Screen == {{attachment:07-Example-Guest-Grub-Boot-Menu.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 96: | Line 85: |
| 7) Example Installed Guest OS Boot Screen 07-Example-Guest-Grub-Boot-Menu.png 8) You can know the assigned IP Address for the Guest OS 08-Find-IP-Address-Guest.png |
== 8) You can know the assigned IP Address for the Guest OS == {{attachment:08-Find-IP-Address-Guest.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 108: | Line 92: |
| 11) Trouble Shoot CDROM issues 11-TroubleShoot-CDROM.png |
9) Trouble Shoot CDROM issues {{attachment:11-TroubleShoot-CDROM.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
| Line 115: | Line 98: |
| 12) Trouble Shoot Boot issues 12-TroubleShoot-Boot.png |
10) Trouble Shoot Boot issues {{attachment:12-TroubleShoot-Boot.png|Create new virtual machine|align="middle"}} |
Running Linux in a VM
Hardware Requirements
You need a system with virtualization (VT-d), at least 4GB of RAM, and 40GB of free hard drive space in order to run Linux in a VM. If you want to download and compile the kernel, you may need additional space of up to 20GB.
Download Debian
Download link to Get a recent version of Debian.
Install Libvirt/Virtual-Manager Virtualizer
Instructions for Debian OS:
Debian setup link Debian Setup and Help Page.
Install the needed packages:
sudo apt-get install qemu-kvm libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon-system virt-manager ebtables
Add your user to libvirt group:
sudo adduser user libvirt
Configure libvirt:
virsh --connect=qemu:///system net-start default virsh --connect=qemu:///system net-autostart default
Start virt-manager from Application Menu.
Instructions for Archlinux:
Install needed packages:
sudo pacman -S virt-manager libvirt ebtables dnsmasq qemu
Add your user to kvm group:
sudo adduser user kvm
Archlinux setup page See this link for further setup further instructions.
Setup Virt Machine Manager
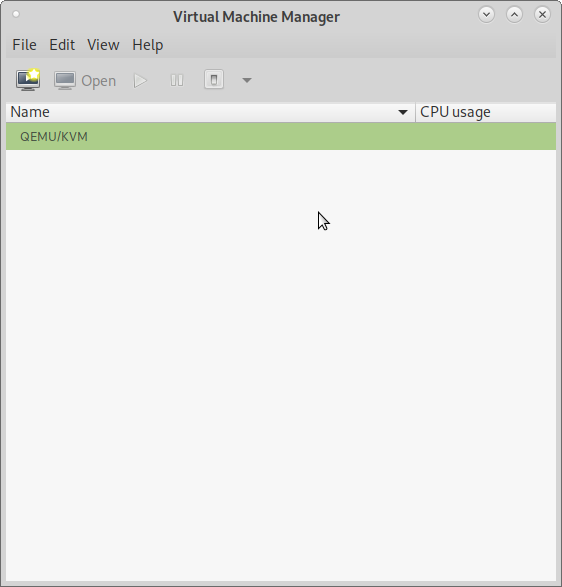
Start Virtual Machine Manager from Application Menu
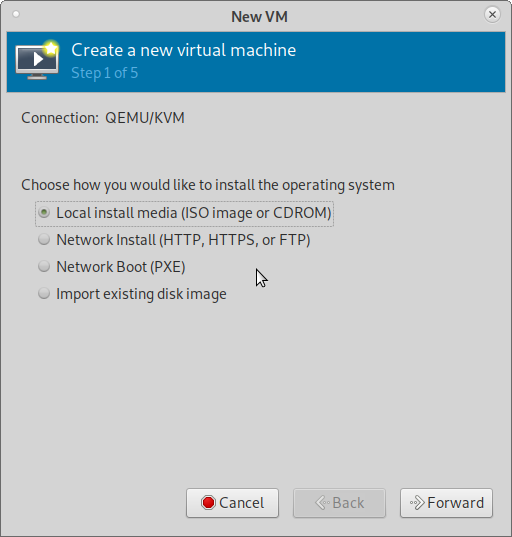
1) Click on "Create a new virtual machine" button for new VM creation
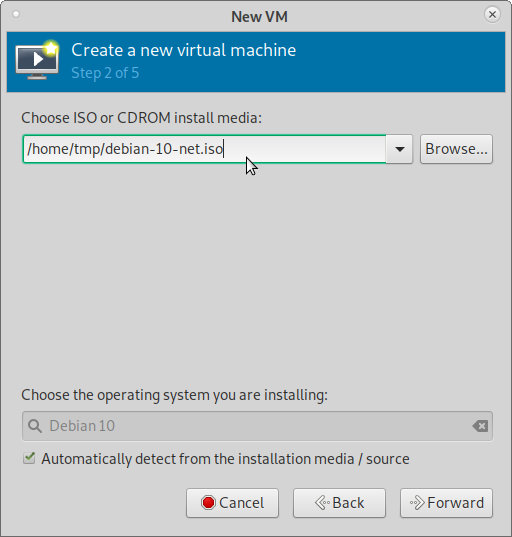
Choose install media (ISO image or CDROM) for installation from your downloaded favourite Linux Distro ISO image.
2) Browse and choose the Linux Distro ISO image
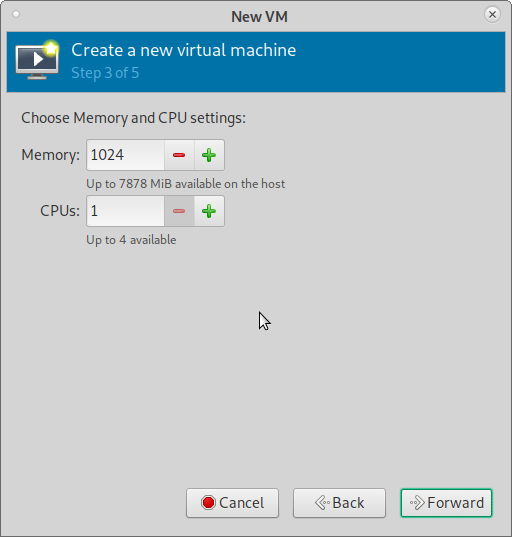
3) Set Your required Memory and CPU settings for the VM (Guest OS)
4) Enable and Create a storage space for the VM (Guest OS)
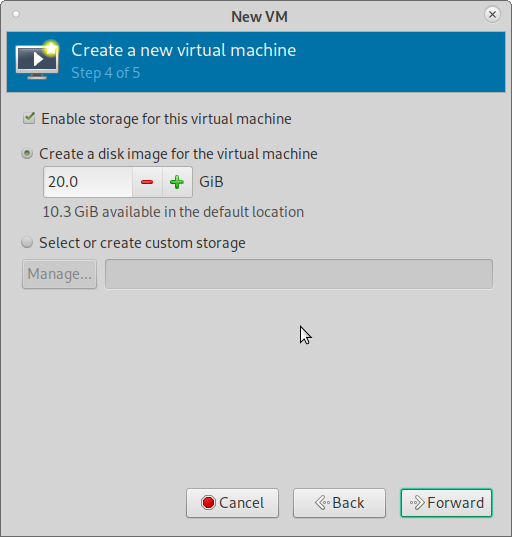
5) Ready to begin the installation
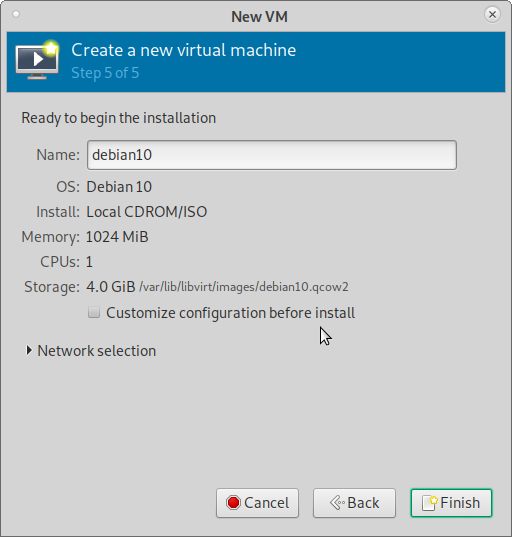
Shows the settings you chose. Put a Name for the VM as you like (App suggests one by default)
Press Finish Button. It creates the VM and boots into it and starts the Linux Distro OS installation.
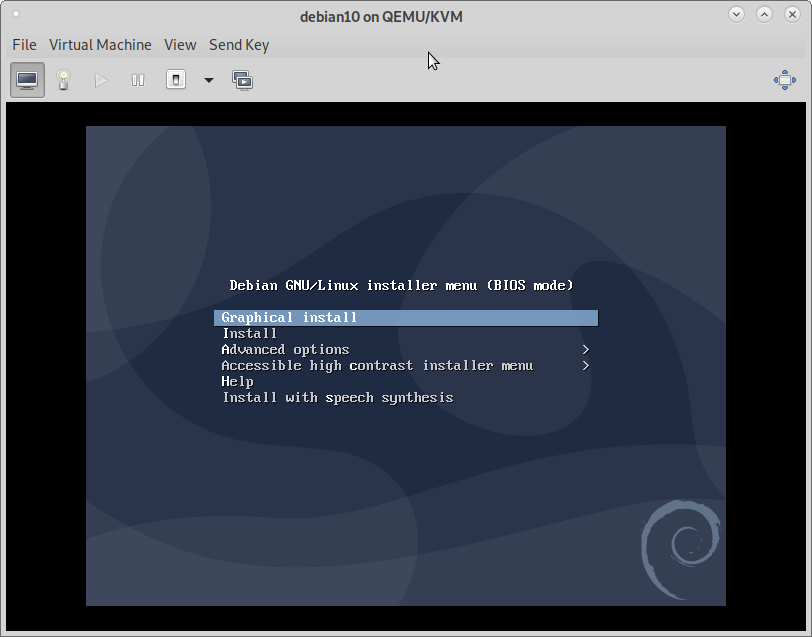
6) Example Linux Distro OS Install Start Screen
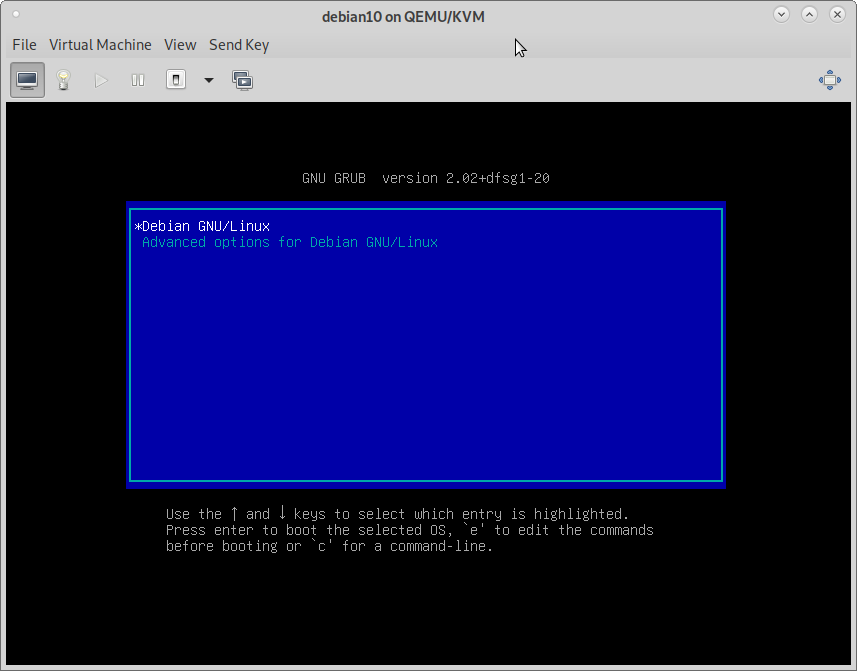
7) Example Installed Guest OS Boot Screen
8) You can know the assigned IP Address for the Guest OS
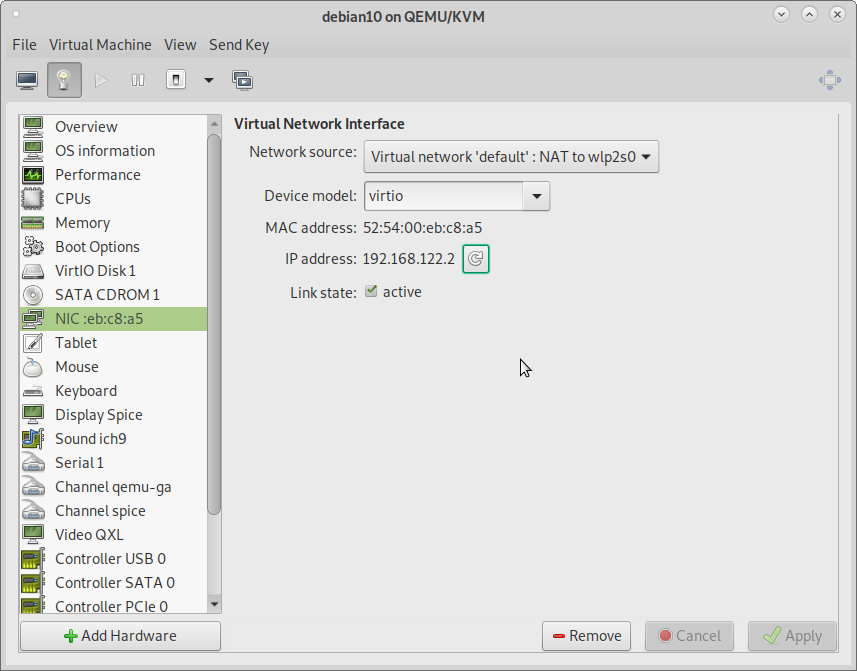
Find your Guest's ip address in "Show virtual hardware details" menu in NIC option. If IP address is not shown click refresh button and see. Mind that the guest OS is running and network is running in guest.
IP address may be needed for ssh access to your Guest OS from host.
9) Trouble Shoot CDROM issues 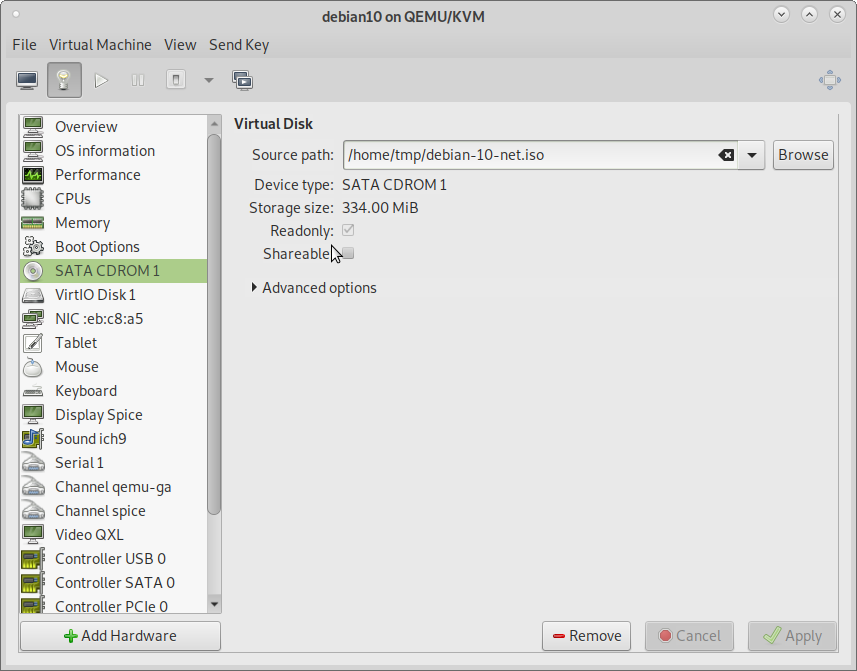
You can check if CDROM ISO image is present and if not browse and select it.
10) Trouble Shoot Boot issues 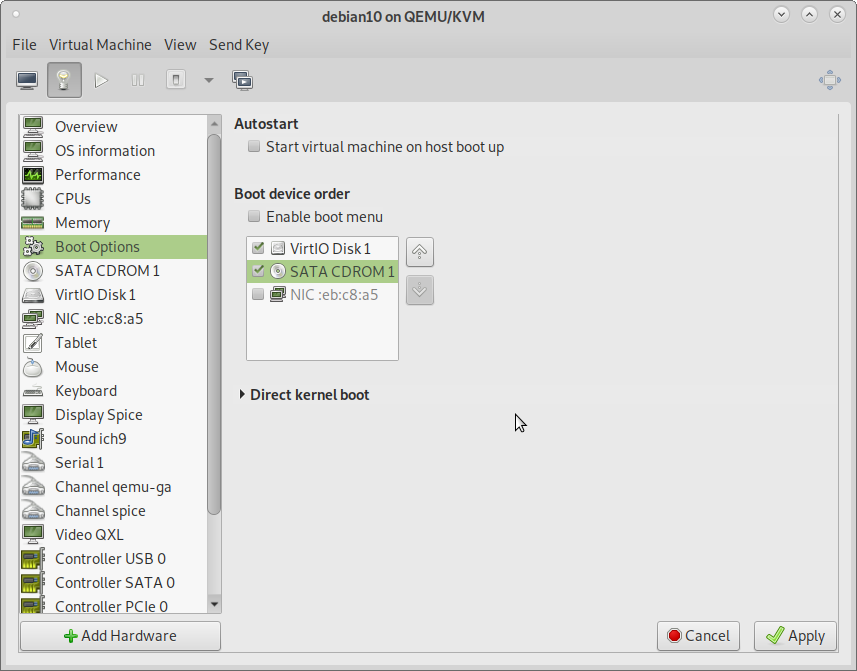
You can set devices to be bootable and the order of boot.
SSH Access
Install ssh (rsync) in both Host and Guest OS
Debian/Ubuntu install instructions:
apt-get install ssh rsync
Find your Guest's IP Address in "Show virtual hardware details" menu in NIC option. If IP address is not shown click refresh button and get it. Mind that the Guest OS is running and network is up and running in guest.
For SSH access to Guest OS run:
ssh -p 22 user@ip_address_of_guest
You can access guests with their hostnames. See this link for instructions for Debian.